The renewal of relations between Saudi Arabia and Iran is unlikely to have a detrimental impact on Israel
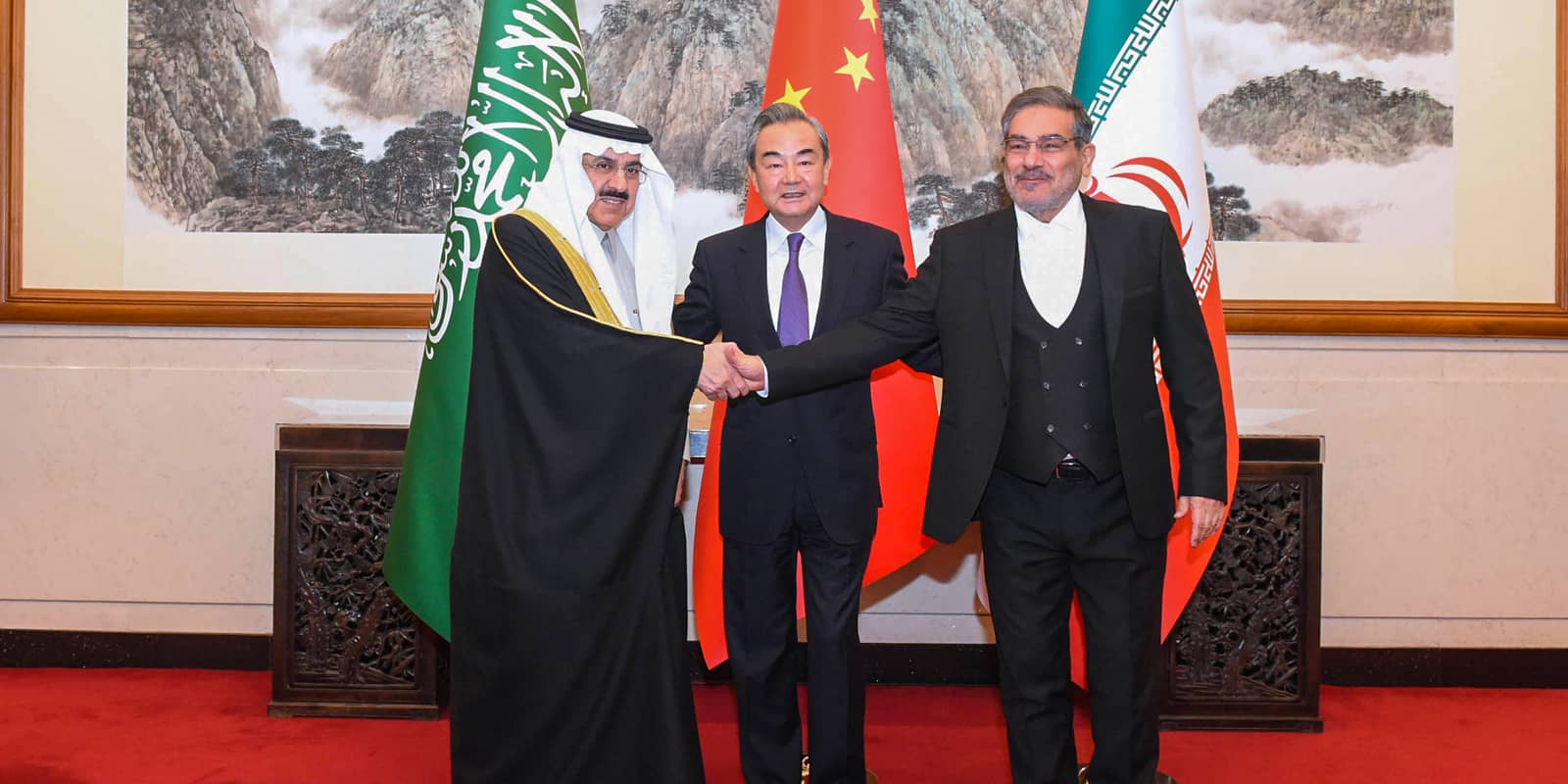
On March 10, 2023, Iran and Saudi Arabia officially announced the renewal of diplomatic relations. This news, along with a subsequent meeting between representatives from Iran and the United Arab Emirates, and talks between Iranian representatives and those from Bahrain, has attracted much attention.
The reasons behind the renewed reconciliation between Saudi Arabia and Iran
Two main reasons contributed to the shift in Saudi policy towards Iran. First, the strained relations between Saudi Arabia and the US Democratic administration led by President Joe Biden played a significant role. During the presidential election campaign, Biden referred to Saudi Arabia as a “pariah state” due to the murder of Jamal Khashoggi in 2018. After taking office, Biden maintained a cold and alienating attitude toward Saudi Arabia. In February 2021, just a month after entering the White House, Biden announced the cessation of American aid to the Saudi military operation in Yemen, including a ban on the sale of certain weapons. That was a significant move considering Saudi Arabia is the world’s largest purchaser of American weapons.
Saudi Arabia observed the American administration persistently pursuing the renewal of the nuclear agreement with Iran, proposing extensive concessions instead of imposing severe economic sanctions on Iran as an American initiative. The US also did not take the lead in efforts at the UN Security Council to renew the package of sanctions against Iran within the framework of the nuclear agreement (Snapback) nor increase the level of military threats against Iran. That only exacerbated the political tensions and mistrust between Saudi Arabia and the United States.
Saudi Arabia’s foreign and security policy was another critical factor in renewing relations with Iran. The Saudi government has always prioritized maintaining diplomatic and political ties with all nations, even with its biggest rival. In the case of Iran, Saudi Arabia recognizes that it does not possess a strong enough military to challenge the regional Shiite power. Therefore, Riyadh aims to limit its confrontation with Iran to a “rivalry” rather than escalate to war and maintain low military intensity. The primary objective of Saudi Arabia in the Iranian context is to avoid military conflict with Tehran while allowing Israel and the US to lead the military and espionage efforts. Saudi Arabia seeks to influence both nations from a “safe” distance.
Although Saudi Arabia and Iran have renewed their relations, it is unlikely that they will agree on ending the conflict in Yemen, currently fought through proxies. The war began before the severance of contact between the two countries and is expected in the near term to continue, interspersed with temporary ceasefires. Furthermore, Saudi Arabia will not be willing to accept Iran’s pursuit of nuclear weapons, as this poses a significant threat to its national security and would provide Iran with a significant strategic advantage.
Even after the renewal of relations, Saudi Arabia and Iran will continue to view each other as rivals and maintain cautious political dealings characterized by respect and suspicion.
The Implications for Israel
The resumption of ties between Saudi Arabia and Iran is unlikely to affect the relationship between Saudi Arabia and Israel. Jerusalem and Riyadh maintained clandestine ties over the past decade despite Saudi Arabia keeping diplomatic relations with Iran before 2016. Thus, there is no indication that the renewal of ties with Iran will alter Saudi Arabia’s stance toward Israel.
Saudi Arabia and Iran remain rivals because both Muslim powers compete for regional dominance, and differ on religious grounds as Sunnis versus Shias.
Maintaining good relations with Israel is of great interest to Saudi Arabia, particularly concerning their joint efforts to counter Iran’s nuclear program. Israel is the only country in the world that takes military action against Iran’s aggression, especially regarding their nuclear program, except for rare instances where the US intervenes, mainly in response to attacks on its troops by Shia militias supported by Iran in Syria. Saudi Arabia is well aware of this and appreciates Israel’s military initiatives.
Saudi Arabia also recognizes the importance of its relationship with Israel in gaining influence in Washington and bolstering Mohammed bin Salman’s standing before the Senate and Congress. That is especially crucial given the hesitancy of some Democratic elements to engage with MBS in light of the Saudi government’s role in the murder of journalist Jamal Khashoggi. Bin Salman hopes that Israel can help him lift the American embargo on selling advanced weapons systems to Saudi Arabia, particularly in light of Iran’s rapid military nuclear progress.
Moreover, the Abraham Accords, signed with the support of Saudi Arabia, are viewed as a significant geopolitical asset for the Sunni kingdom. These agreements contribute to regional stability and the Gulf partners’ economic growth. Saudi Arabia can leverage its role as a regional power broker in promoting peace agreements. As such, it has a vested interest in expanding the Abraham Accords, even if it has not yet taken part directly.
JISS Policy Papers are published through the generosity of the Greg Rosshandler Family.
Photo: IMAGO / Xinhua









 - בניית אתרים
- בניית אתרים